Research areas
Research areas are the sub-national units of analysis where most of the data collection is concentrated. They can be a town, part of a city or a rural district.
The use of research areas reflects the overall emphasis of MIGNEX on disaggregation in the study of migration–development connections and policies. By examining local contexts, it is possible to assess specific, local drivers and consequences of migration, as well as the drivers and consequences experienced at the national level.
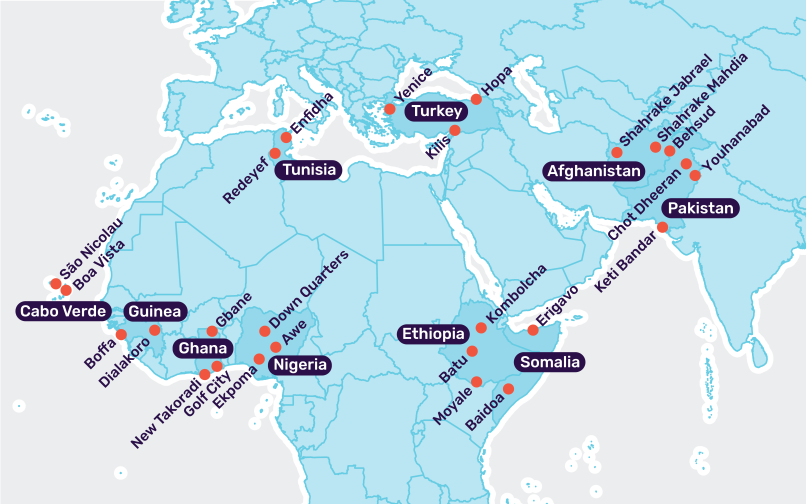
The population of research areas are in the range of 10,000 – 100,000. Each area is sufficiently small enough to experience the same specific developments and conditions but some are diverse in socioeconomic terms. The project will collect data in 25 research areas spread across ten case countries. The project team is also preparing for data collection in an additional 26th area in order to strengthen the data and have a safety margin for unforeseen obstacles.
MIGNEX Research Areas
The following are the MIGNEX research areas. The selection ensures a complementarity of research areas across the entire project as well as within each country. The areas have also been prioritized on the basis of their consistency with the notion of research areas in the MIGNEX research design. In other words, they are appropriately sized and reasonably self-contained areas where we can expect causes and consequences of migration to interact.
The specific developments of each area are ‘presumed’ in the sense that they will need to be verified by the data that we collect. In this process we might identify additional specific development, for instance related to changes in security.
The satellite photos in this document are all from the same altitude and therefore cover an area of roughly the same size. In most cases, this is just a part of the research area.
Afghanistan
AFG1: Shahrake Jabrael
Shahrake Jabrael is a peri-urban area located to the west of the city of Herat. While small scale infrastructure developments in recent years - roads, new shops - have improved livelihoods to an extent, the area has not seen any outside investment or international programming. This research area represents protracted stagnation, providing a contrast with other selected research areas in Afghanistan. This is a self-contained area, with the majority of people living in the township also working and accessing services in the same area. The estimated population is around 40,000 people.
AFG2: Behsud
Behsud is a peri-urban area on the outskirts of Nangahar city. An influx of returnees from Pakistan has led to urban growth, industrialization, and livelihood expansion, sustained by major social protection reforms through the World Bank-funded Citizen’s Charter. There is significant of internal displacement due to conflict.
AFG3: Shahrake Mahdia
Shahrake Mahdia is a township within Kabul of around 60,000 residents. It was developed in the past two decades and has experienced significant infrastructure improvements in the past decade in the form of roads and access to transportation, rapid construction of new high schools (including private and public schools) and installment of electricity in the township. This expansion has had an impact on air pollution. Shahrake Mahdia is a place of settlement for returning migrants from Pakistan and Iran, as well as for IDPs and rural-urban migrants seeking to move towards Kabul.
Cabo Verde
CPV1: São Nicolau
São Nicolau is a mountainous agricultural island in the north of Cabo Verde. It has seen a gradual population decline and marginalization, compounded by weakened connectivity to the rest of the country. There has been continuous out-migration to other islands and abroad, and remittances per capita are higher than on any other island.
CPV2: Boa Vista
Boa Vista is an arid and sparsely populated island known as ‘the island of dunes’. It was a backwater but has seen massive growth in tourism since the international airport opened. There was traditionally out-migration to other islands and abroad, but Boa Vista is now a destination for internal and international migrants.
Ethiopia
ETH1: Kombolcha
A growing town close to the larger city of Dessie, Kombolcha has historically been an area of industry, with an older national textile as well as a beer factory present in the town. A new and modern industrial park established in 2017 has brought international investment to Kombolcha, constituting an important livelihood expansion for the area. This has also led to infrastructure expansion, including the Kombolcha airport and a forthcoming railway line leading towards Djibouti. Kombolcha has been the seat of both rural to urban in-migration, as well as seeing significant migration outflows in particular of women towards the Middle-East and Gulf countries.
ETH2: Batu
Batu is a small city in the Oromia region, on the main road to Addis Ababa. The city is a centre of large foreign-owned flower farms and other agribusinesses that have created substantial employment. The area suffers from land degradation and pollution of the Ziway lake. There is significant out-migration of women to the Middle East.
ETH3: Moyale
Moyale is a town on the border with Kenya. This part of Oromia region has been in a situation of protracted stagnation, made worse by sporadic but growing violence between Somali and Oromo populations. Moyale is a transit point for Ethiopians emigrating across the southern border, and also itself a source of migrants on this route.
Ghana
GHA1: Gbane
Gbane is a rural area in the Upper East region, made up of a number of small-scale mining communities. Chinese investment in mining has contributed to livelihood expansion. The area suffers from frequent drought and land degradation. Young people migrate south to work in urban areas, but the area also hosts labour migrants from surrounding rural areas.
GHA2: Golf City
Golf City is an urban area in the Greater Accra region, on the outskirts of the port city Tema. It is named after the nearby golf course and is the site of recent investment in industrial, infrastructure and utilities projects. There is also a new private university. Inhabitants of Golf City include domestic and international migrants.
GHA3: New Takoradi
New Takoradi is a small town that has developed on the outskirts of the port city of Takoradi. It serves both as a dormitory town and as an industrialized zone. Coastal erosion is a problem. Traditional fishing is negatively affected by new construction for the port as well as by declining fish stocks. There is substantial emigration, including attempts at stowing away on ships.
Guinea
GIN1: Boffa
Boffa is a town in the Boke region near the mouth of the Pongo river. The town has a fishing port, and is a trading centre for fish, rice, bananas and palm oil. The fishing industry is in decline, partly due to the environmental impact of mining and overfishing by foreign fleets. There are plans to build a railway line Boffa.
GIN2: Dialakoro
Dialakoro is a rural area along the Niger river in the Kankan region, near the border with Mali. The area has insufficient provision of basic services and has seen little development. There is a shortage of arable land, particularly for cashew nut cultivation, and have been conflicts over land. The World Bank Guinea Integrated Agricultural Development Project is supporting the agricultural sector. There is substantial migration towards Europe.
Nigeria
NGA1: Down Quarters
Down Quarters is a mixed residential and business neighbourhood in Kaduna, made up partly by former railway workers’ housing. It is located between the railway line and Kaduna river and is prone to flooding. Down Quarters abuts the recently opened Kaduna Inland Dry Port, which has brought trade and jobs to the area. The city has seen religious conflict in recent years.
NGA2: Awe
Awe is a rural area in Nasarawa state, dominated by farming and petty trade. There is also artisanal bauxite mining, with harmful environmental impacts. Awe is one of the areas in which a flagship programme of conditional cash transfers is being rolled out. The programme, which is funded in part by the World Bank, initially targets particularly poor areas.
NGA3: Ekpoma
Ekpoma is a small university town in Edo state. The state has high levels of out-migration and is known as a centre of trafficking in persons. A large number of Technical and Vocational Education and Training programmes have been implemented, partly to address migration pressure.
Pakistan
PAK1: Chot Dheeran
Chot Dheeran is a small town in Punjab province, surrounded by fields and smaller villages. There is considerable private wealth, much of it derived from migration, but poor public services and limited economic activity. The area is a steady source of emigrants, including some who travel irregularly towards Europe via Iran and Turkey.
PAK2: Youhanabad
Youhanabad is an area stretched over two kilometers along Ferozpor Road in the Northeast of Lahore. This is a majority Christian area, where Christian and Muslim communities live together. The infrastructure in the area is limited and there is clear need for investment. However, there is a major gas pipeline which crosses Youhanabad, provided by the government. The area is affected by environmental degradation due to a lack of a proper public sewage system. This is an area, which over time has attracted internal migration of Christians from all parts of Punjab.
PAK3: Keti Bandar
Keti Bandar is an old port town in Sindh province, near the mouth of the Indus river, with a hinterland of agricultural villages. Sea water intrusion has been damaging to agriculture, and the traditional fishing industry has been marginalized by large-scale industrial fishing. There is substantial out-migration, primarily to other parts of Pakistan rather than abroad.
Somalia
SOM1: Erigavo
Erigavo town is the capital of Sanaag, an isolated, semi-arid pastoral region of Somaliland. Income from livestock has declined considerably as a consequence of droughts. Erigavo is a node on migration routes to Ethiopia. The area hosts a large population of internally displaced people.
SOM2: Baidoa
Baidoa is city in Bay region in southern Somalia. It is a focus of development, humanitarian and stabilisation initiatives and showcases integrated programming achievements. It is also a target donor-funded infrastructure investment and has seen major improvements to its roads and housing. The area hosts large numbers of internally displaced persons as well as returnees.
Tunisia
TUN1: Enfidha
Enfidha is a town in Sousse Governorate, a few kilometres inland from the Gulf of Hammamet. It is a formerly rural locality that has seen rapid transformation, including the establishment of an industrial park. An international airport opened in 2009 and a deep-sea port is under construction.
TUN2: Redeyef
Redeyef is a phosphate mining town in Gafsa Governorate, near the Algerian border. Mining production has fallen significantly, and the town has seen frequent labour strikes and demonstrations. Unemployment levels are very high.
Turkey
TUR1: Hopa
Hopa is a town in a remote area of northeastern Turkey, close to the Georgian border. It has benefitted from policy measures that have stimulated cross-border economic activity, as well as from construction of highways and dams. The area now hosts many return migrants from Turkish cities.
TUR2: Yenice
Yenice is a rural town and district in the Marmara region. Infrastructure development in the area include the construction of highways and power plants, which has hurt rather than expanded livelihoods as a result of expropriation, land-grabbing and environment degradation.
TUR3: Kilis
Kilis is a town near the Syrian border that has traditionally benefitted from cross-border trade. However, the volume of trade has fallen sharply as a result of the Syrian civil war. The town hosts a very large population of Syrian refugees and has also grown from rural-urban migration.